
For example, the neutral bromine atom, with 35 protons and 35 electrons, can gain one electron to provide it with 36 electrons. Atoms of group 17 gain one electron and form anions with a 1− charge atoms of group 16 gain two electrons and form ions with a 2− charge, and so on. When atoms of nonmetal elements form ions, they generally gain enough electrons to give them the same number of electrons as an atom of the next noble gas in the periodic table. The name of a metal ion is the same as the name of the metal atom from which it forms, so Ca 2+ is called a calcium ion. It has the same number of electrons as atoms of the preceding noble gas, argon, and is symbolized Ca 2+. This results in a cation with 20 protons, 18 electrons, and a 2+ charge. For example, a neutral calcium atom, with 20 protons and 20 electrons, readily loses two electrons. To illustrate, an atom of an alkali metal (group 1) loses one electron and forms a cation with a 1+ charge an alkaline earth metal (group 2) loses two electrons and forms a cation with a 2+ charge, and so on. Atoms of many main-group metals lose enough electrons to leave them with the same number of electrons as an atom of the preceding noble gas. You can use the periodic table to predict whether an atom will form an anion or a cation, and you can often predict the charge of the resulting ion.
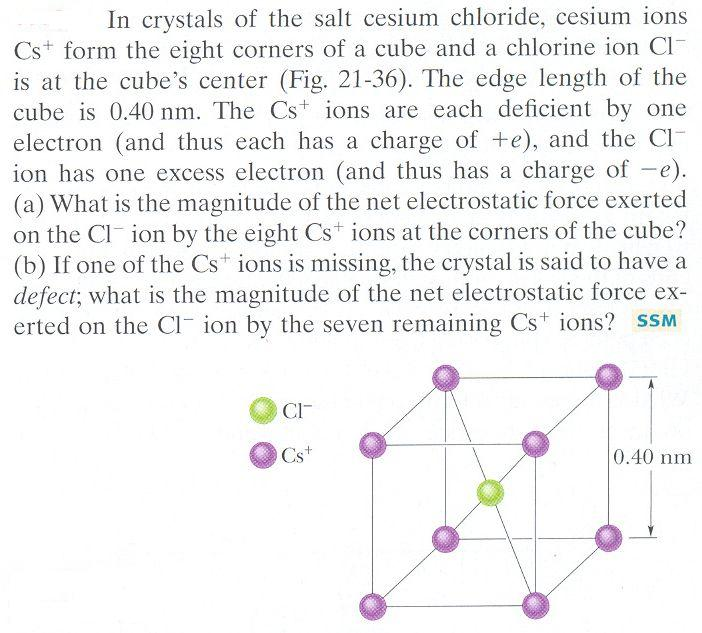
Caesium ion charge plus#
(b) A sodium cation (Na +) has lost an electron, so it has one more proton (11) than electrons (10), giving it an overall positive charge, signified by a superscripted plus sign. Figure 2.28 (a) A sodium atom (Na) has equal numbers of protons and electrons (11) and is uncharged.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
